A team of researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles aided by a computer model, has identified 121 possible sites for Ashoka rock edicts, many of which are in the Deccan Plateau.
Currently, 39 Ashokan edicts are known. There are pillar edicts and rock edicts and these edicts are located at sites ranging from Afghanistan to the Gangetic plains to the eastern coast of India. The UCLA study suggests several new sites in the Deccan Plateau, in Afghanistan-Pakistan border areas and northwest India. Only archeological excavation of these sites could reveal if there are more Ashokan edicts, unknown to history so far.
The stone inscriptions ascribed to Ashoka, the 3rd-century BC ruler of the Mauryan dynasty, are important for several reasons. They constitute the first decipherable written documents in the Indian subcontinent coincident with the development of urbanism.

The emplacement of Ashokan edicts as an act of royal proclamation is interpreted as the evidence of the first substantial unifying political regime of the subcontinent. Finally, the edicts are the first tangible expression of religious practices related to Buddhism.
Read More: Mystery of 1600 years old Iron Pillar of Delhi
Practising Buddhism began in 6th century BC, but its visibility increased with the imperial sanction provided by Ashoka’s proclamations.
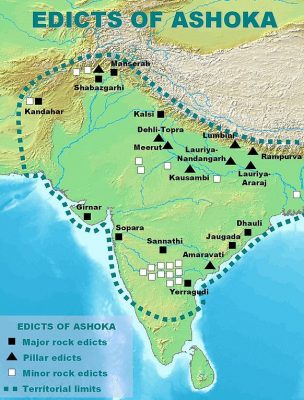
The UCLA team first used the computer model to correctly identify the known Ashokan sites. Then, they exploited the same tools to check if there could be other possible sites. The model threw up as many as 121 sites.
“The final data are probability maps and we identified 121 locations that are similar to known inscriptions. These locations are hypotheses that can be tested and accepted or rejected like any other theory in science,” lead researcher Thomas Gillespie told DH.
The results suggest Ashoka edicts were not randomly placed and most of the recent edicts discovered have only been found by chance.
“We believe that a search for edicts in any of these locations would yield a higher-than-average probability of finding new inscriptions,” the researchers commented in a research paper, which would be published in the journal Current Science.
The computer model they picked up for the study is generally used for understanding the species distribution among animals. But it was handy while searching the rock edict sites because of its ability to handle variation in geographical parameters. The performance of the model can be improved with additional inputs on the political influence, ethnicity and linguistics pattern of the Ashoka era.



