The Bhimbetka rock shelters are the collection of 750 rock shelters from which 500 are inwrought by the paintings. Situated in the Raisen District of Madhya Pradesh of India, these Stone Age rock paintings are around 30,000 years old. It is one of the largest repositories of prehistoric art in India.
The shelters were designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2003. In addition to the cave paintings, archaeologists have unearthed large numbers of artifacts in the caves and in the dense teak forests and cultivated fields around Bhimbetka, the oldest of which are Acheulean stone tool assemblages.
The Bhimbetka shelters exhibit the earliest traces of human life in India. A number of analyses suggest that some of these shelters were inhabited by hominids like Homo erectus more than 100,000 years ago. Some of the Stone Age rock paintings found among the Bhimbetka rock shelters are approximately 30,000 years old ( Paleolithic Age).
The name Bhimbetka is associated with Bhima, a hero-deity of the epic Mahabharata. The word Bhimbetka is said to derive from Bhimbaithka, meaning “sitting place of Bhima“. It is believed that when the five brothers, called Pandavas, were banished from their kingdom, they came here and stayed in these caves, the massive rocks seating the gigantic frame of Bhima, the second Pandava. However, these claim still remains to be corroborated with concrete evidence.

The caves were eventually discovered in 1957-58 by accident. An archaeologist from Ujjain, Dr. Vishnu Wakankar, strayed too far from the beaten path and found himself amidst this prehistoric treasure trove. Since then more than 700 such shelters have been identified, of which 243 are in the Bhimbetka group and 178 in the Lakha Juar group. Between 1972 and 1977 excavation undertaken by Wakanakar, Misra and Hass revealed a continuous sequence of Stone Age cultures from the late Acheulian to the late Mesolithic and also some of the world’s oldest stone walls and floors.
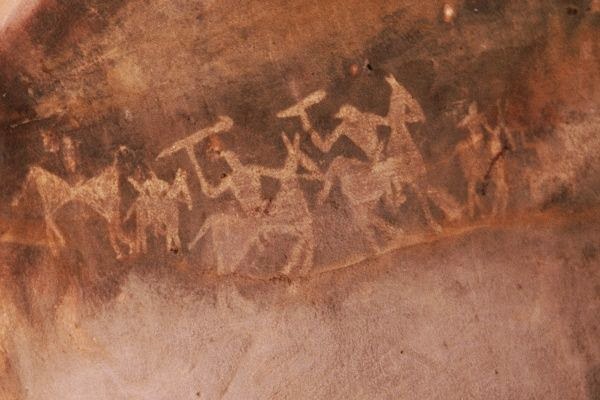
The caves have evolved over time into excellent rock-shelters, ideal sites for aboriginal settlements. The smooth shape of the rocks has led some scientists to believe that the area was once under water. The rocks have taken on incredible shapes in several stunning hues and textures. Apart from the central place the aboriginal drawings have in human history, the caves themselves offer interesting material for a study of the Earth’s history.
Executed mainly in red and white, with the occasional use of green and yellow with themes taken from the everyday events, the scenes usually depict hunting, childbirth, communal dancing, drinking, religious rites, burials, horse and elephant riders, animal fights, honey collection, decoration of bodies, disguises, masks and different type of animals etc. It depicts the detail of social life during the long period of time, when man used to frequent these rock shelters. The entire area is covered by thick vegetation, has abundant natural resources in its perennial water supplies, natural shelters, rich forest flora and fauna, and bears a significant resemblance to similar rock art sites such as Kakadu National Park in Australia, the cave paintings of the Bushmen in Kalahari Desert, and the Upper Paleolithic Lascaux cave paintings in France.
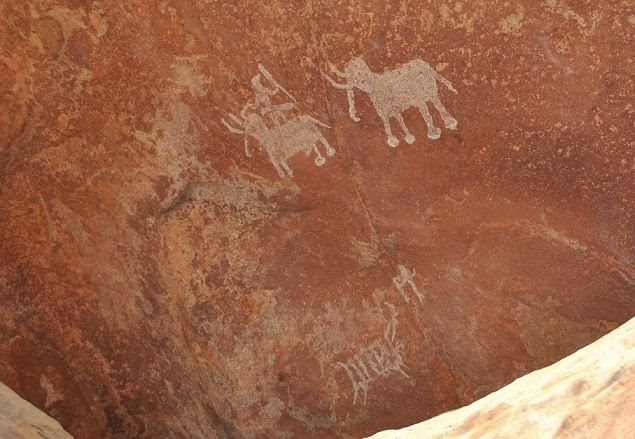

One rock, popularly referred to as “Zoo Rock”, depicts elephants, sambar, bison and deer. Paintings on another rock show a peacock, a snake, a deer and the sun. On another rock, two elephants with tusks are painted. Hunting scenes with hunters carrying bows, arrows, swords and shields also find their place in the community of these pre-historic paintings.

It is a marvel that the paintings have not faded even after thousands of years. The colors used by the cave dwellers were prepared by combining manganese, hematite, soft red stone and wooden charcoal. Perhaps, animal fat and extracts of leaves, vegetables, and roots were also used in the mixture. Brushes were made of pieces of fibrous plants. The natural pigments have endured through time because the drawings are generally made deep inside a niche or on inner walls. Some of the geometric figures date to as recently as the medieval period.
The rock art of Bhimbetka has been classified into various groups on the basis of the style and subject. The superimposition of paintings shows that different people used the same canvas at different times. The paintings, which display great vitality and narrative skill, are categorized into different prehistoric periods. The oldest are dated to the Late Paleolithic Period (Old Stone Age) and consist of large linear representations of rhinoceroses and bears. Paintings from Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) times are smaller and portray, in addition to animals, human activities. Drawings from the Chalcolithic Period (early Bronze Age) showcase the early humans’ conceptions of agriculture. Paintings from Early Historic perioddepict religious motifs, including tree gods and magical sky chariots. Medieval paintings are geometric, linear and more schematic but show degeneration and crudeness in their artistic style.
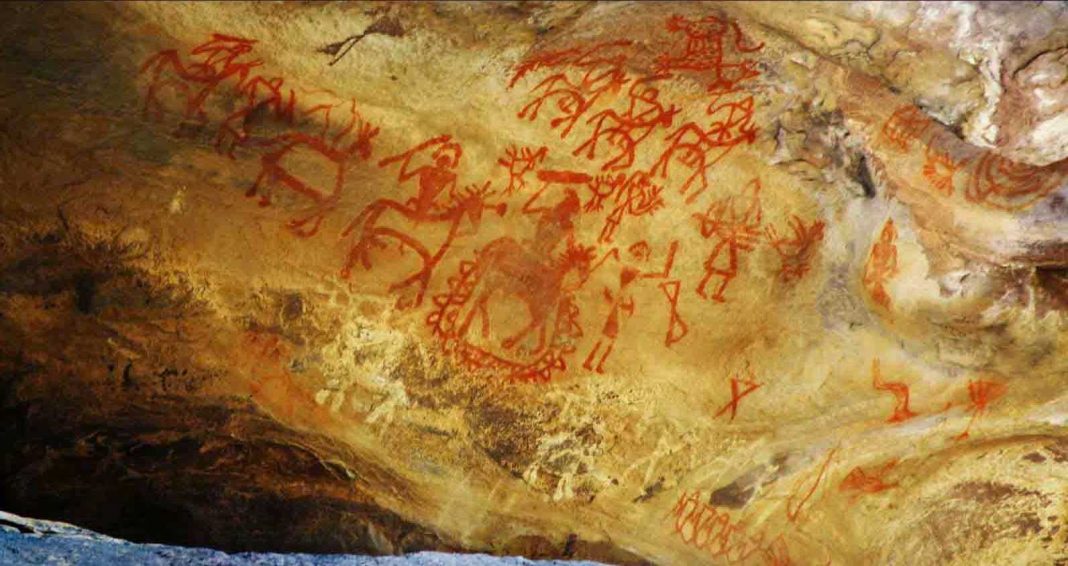




our honble gondwana gondi sahitycharya dr. motiravan kangali gondi language expert have deciphered hampi rock pictographic script painting with the help of gondi protodravidian language root marphemes